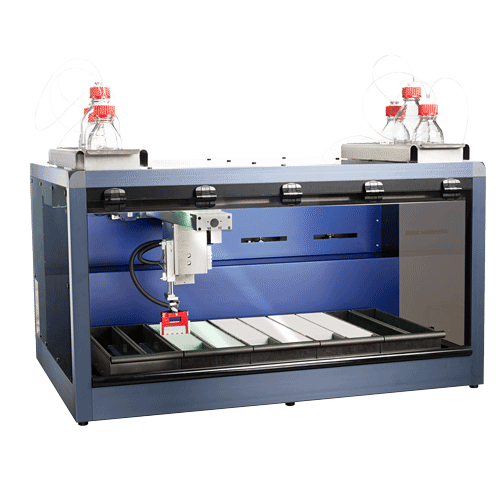


LC-MS联用技术-全自动干血斑分析系统
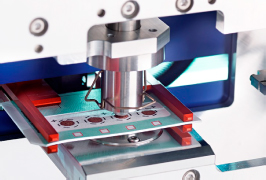
干血斑 (DBS) 分析提供了相对传统液体采样技术的明显优势:更少的侵害、所需样品更少,并可在室温下长时间储藏、污染风险也较少。然而,对于诊断 TLC 分析,处理大量 DBS 样品制备、储存和管理对研究者来说是一项巨大的挑战。 通过配置自动提取 DBS (干血斑) 卡片,CAMAG DBS-MS 500 能轻易在短时间内自动且可靠地筛选多个血样。与传统血样或血浆手动收集和分析方法相比,它大大简化了血样收集过程、降低成本和风险,是用于 LC-MS / MS (质谱) 分析的高效样品前处理仪器。
- 在 3 分钟内常压条件下全自动快速处理多达 500 张 DBS卡片。
- 通过 DBS-MS 500 可靠的机械臂和最新研发的夹取工具进行精确光学DBS 卡片斑点定位。
- 集成条形码阅读器设备用于准确的卡片识别。
- 自动化内标 (IS) 应用模块可在 LC-MS 分析之前直接应用。
- 可靠的清洗站消除残留困扰。
- 与任何 LC-MS 系统轻松集成连接,提供了极佳的灵活性,并在各种不同实验室环境下简便应用。

HPTLC PRO
攻克重现性难题,开启薄层色谱新纪元
全自动薄层样品分析及评价系统,无人干预封闭式在线全流程自动化运作,点样、展开、衍生化、检测、分析、报告,一步到位。尤其适用于复杂成分样品的分析检测。
